Source(s): Randy Drinkard
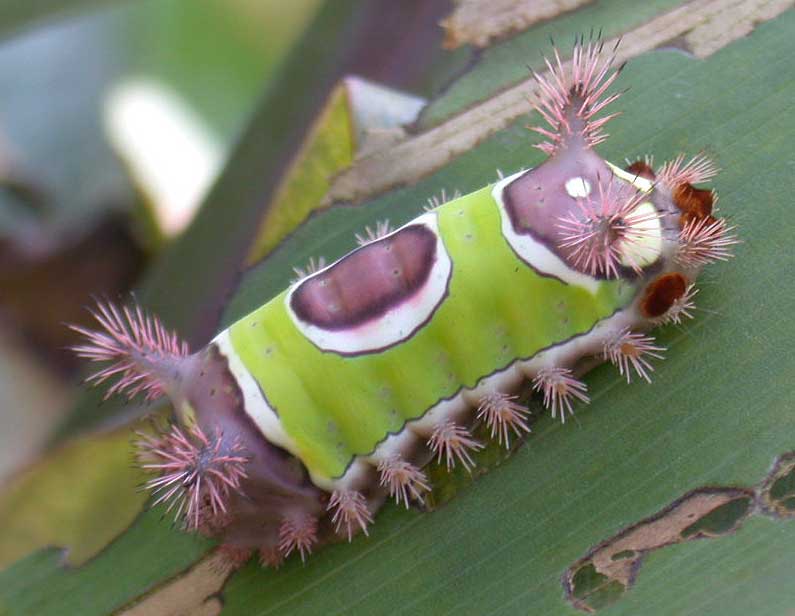
Over the past several weeks I have been contacted by several community gardeners who have discovered saddleback caterpillars by feeling their painful sting. I was stung by one years ago while harvesting okra. It literally knocked me to the ground. To avoid more gardening mishaps with these creatures I want to share this article written by Randy Drinkard. Stay safe out there gardeners!
Most people know that bees, wasps, hornets and some ants can sting to defend themselves or their nests. Only a few people realize, usually from first hand experience, that handling some caterpillars can produce some painful results. Recognizing the few stinging caterpillar species, including the saddleback, may prevent irritating encounters.

Saddleback Caterpillar Description
The saddleback caterpillar measures about an inch long, and has poisonous spines on four large projections (tubercles) and many smaller ones projecting from the sides of its body. The “saddle” consists of an oval purplish-brown spot in the middle of a green patch on the back.
The saddleback caterpillar is a general feeder and is generally found on many hosts including corn foliage, apple, pear, cherry, rose, Pawpaw, basswood, chestnut, oak, plum and other trees in late summer.
Diagnosing and Treating Stings
Diagnosis is usually simple since a rash generally breaks out where the hairs or spines have made skin contact. Contacting the hollow poisonous hairs or spines (connected to underlying poison glands) causes a burning sensation and inflammation that can be as painful as a bee sting. The irritation can last for a day or two and may be accompanied by nausea during the first few hours. Usually the site of contact reddens and swells much like a bee sting.
Immediate application and repeated stripping with adhesive or transparent tape over the sting site may be helpful in removing broken hairs or spines. Washing the affected skin area thoroughly with soap and water may help remove irritating venom. Prompt application of an ice pack and a baking soda poultice should help reduce pain and swelling. Household analgesics, such as aspirin, appear to be ineffective for reducing pain and headache. However, oral administration of antihistamines may help relieve itching and burning. Topical corticosteriods may reduce the intensity of inflammatory reaction. Desoximetasone gel applied twice daily to affected areas may also help. Prompt referral to and treatment by a physician should be made when severe reactions are evident. Very young, aged or unhealthy persons are more likely to suffer severe reaction symptoms.
Sting Prevention
Occasionally, these stinging hair caterpillars may drop out of trees onto people, crawl into clothing on the ground, occur on outdoor furniture or sting when brushed against on plant foliage. Be careful when attempting to brush them off. Never swat or crush by hand. Remove them carefully and slowly with a stick or other object.
Individuals, especially children, should be cautioned about handling or playing with any colorful, hairy-like, fuzzy caterpillars since it is sometimes difficult to distinguish between harmless and venomous insect larvae. Never handpick these hairy, fuzzy or spiny caterpillars except with heavy leather gloves if necessary. Wear long sleeve shirts, trousers and gloves when harvesting sweet corn or working in the landscape in late-summer and early-autumn to reduce possible stings.
Chemical Control
Usually, these stinging hair caterpillars do not occur in sufficient numbers to warrant the use of pesticide sprays. Should potential hazards exist around residences or schools, infested shrubs and trees may be sprayed to reduce or eliminate these caterpillars. Sprays of carbaryl (Sevin), or Bacillus thuringiensis (Biotrol WP, Sok-bt, or Thuricide) as well as various pyrethroids (bifenthrin, cyfluthrin, cypermethrin, deltamethrin, lambda-cyhalothin, permethrin and tralomethrin) in formulations labeled for bushes, shrubs and trees, can be helpful, if practical. Be sure to read the label, follow directions and safety precautions.
Resource(s):
Insect Pests of Ornamental Plants
Center Publication Number: 200