Sharon Dowdy is a news editor with the University of Georgia College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences

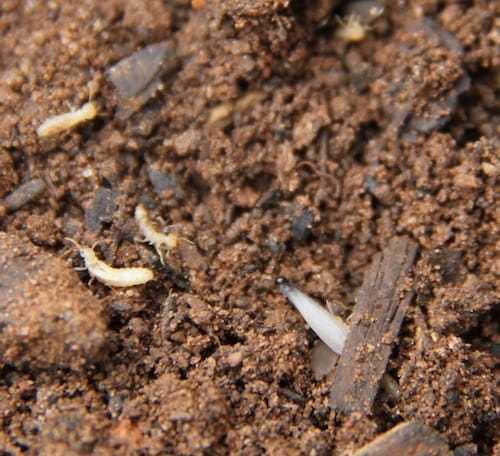
Those who tackle termites may think the tiny insects spend their days eating wood. But a University of Georgia entomologist says 80 percent of the time they do absolutely nothing.
“As a group, they always look busy. But as individuals, only a few of them actually spend their time digging,” said Brian Forschler, a researcher with the UGA College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences.
To control a pest, you first have to know how if operates: its likes and dislikes, what it eats, where it lives, its enemies, etc. Over the years, researchers have made great strides into understanding termite behavior, said Forschler who has studied termites for more than 20 years.
“In the late 1800s to early 1900s they were called white ants. In the 1920s, scientists placed them in a special order (Isoptera) apart from ants. In 2007 they were identified as social cockroaches and classified in the order Blattodea that contains roaches,” Forschler said. “So you see, science isn’t written in stone. It’s constantly being questioned.”

Forschler collects termites in wooden bait traps, takes them back to his Athens laboratory and watches them in action.
“We put sections of 4-inch PVC pipe in the ground, and fill (them) with wooden sandwiches. The problem is figuring out what happens while we aren’t there – we are just getting a snapshot view of their lives,” he said.
Over the years, Forschler has tracked termite colonies, collected termites, dyed them blue or red and released them to track their movement. And he’s created artificial termite families to see how they interact outside their home nests.
In one study, his then graduate student Jeff Whittman placed six groups of termites in tiny arenas and video taped their behavior for seven days.
“They are simple creatures. They did about 10 things. (They) stood around, moved, chewed, tunneled, cleaned other termites and defecated,” he said. “They’re like cows and other animals that feed on cellulose. They spend time throwing-up and chewing their cud.”
Termites forage for food for themselves and take food from other termites, but they never share their cud, he said.
The UGA research team found termites to be very clean animals.
“We consistently saw them clean each other. A termite doesn’t clean itself, except for its antenna. They depend on their brothers and sisters to clean them,” he said.
Adult termites (the king and queen) can reportedly live for 20 years, and Forschler has termites in his collection that are over 14 years old.
“I have some in my lab that are 13 to 14 years old from logs in Georgia, and they were likely 4 years old when we collected them. A number of different types of social insects live that long. It’s not unusual,” he said.
Forschler’s research has also revealed that termites are not random foragers. They tend to use the same access points over and over.
On test sites, used since 2000 on UGA Athens campus, 83 percent of the infestations identified by Forschler’s team entered buildings using expansion joints, 11 percent followed cracks in stone foundations, 4 percent liked areas where wood was in contact with the ground and 2 percent used the weep holes in brick veneer.
Forschler has identified the following termite traits:
- The queens lay most of their eggs in the spring.
- An average colony contains around 50,000 termites, until they locate a large food resource (like a house, tree stump, or large log). Over the course of a few years that same colony can grow to include hundreds of thousands of termites.
- Termites need a humid environment to survive.
- Five species of subterranean termites are native to Georgia and one invasive species, the Formosan subterranean termite.
- Five of those species swarm and release new adults (kings and queens, called alates) in the late winter and spring (February-May), while one does so in late summer (July-September).
- Colonies move all the time and often don’t return to the same spot.
- Termites have to swallow soil-applied termiticides to die, not just touch the pesticide.
For more information on termites, see these UGA publications:
Biology of Subterranean Termites in the Eastern United States
Identifying the Formosan Subterranean Termite
Termite Control Services: Information for the Georgia Property Owner